Logistics performance and corporate social responsibility (CSR) are increasingly important in today's industrial landscape. Companies striving to optimize logistics operations for efficiency, cost reduction, and improved customer service must also consider their environmental and social impact.
Measuring logistics and CSR performance within a company’s supply chain can prove complex. Existing evaluation methods may lack precision, focus on financial aspects, and neglect environmental or social impacts. The fundamental challenge is designing decision-making tools that integrate logistics and CSR indicators, balancing operational objectives with sustainability imperatives.
In a paper presented at the IEEE International Colloquium on Logistics and Supply Chain Management, researchers address key questions, developing an assessment tool to balance economic goals with sustainability considerations and strategies to ensure effective implementation, resulting in improved logistics performance while upholding CSR commitments.
The Necessity for Better Tools
The interplay between logistics efficiency and CSR initiatives within supply chains necessitates a nuanced approach to performance evaluation and decision-making. Logistics performance metrics, such as delivery times, order accuracy, and inventory turnover, provide valuable insights into operational efficiency but often overlook broader sustainability concerns. Similarly, traditional CSR evaluation frameworks may focus primarily on qualitative social and environmental impact measures, needing more integration with logistical metrics and quantitative performance indicators.
Against this backdrop, developing a decision-making tool tailored to assess CSR and logistics performance emerges as a critical imperative. Such a tool would enable companies to conduct holistic evaluations of their supply chain operations, identify areas for improvement, and align their practices with sustainability objectives and stakeholder expectations. The authors note that by integrating logistics efficiency metrics with CSR indicators, companies can achieve a balanced approach to performance evaluation that reconciles economic imperatives with environmental and social considerations.
By drawing on insights from existing literature, empirical research, and industry best practices, the proposed framework is designed to provide companies with a comprehensive and actionable methodology for assessing and improving their supply chain performance. This practical framework equips professionals with the tools they need to navigate the complexities of determining CSR and logistics performance in contemporary supply chains, underscoring its significance in supply chain management.
The researchers provide a comprehensive background and literature review, highlighting existing research on logistics performance evaluation and CSR assessment. Supply chain management (SCM) has evolved into a critical strategic function for organizations aiming to optimize operational efficiency, reduce costs, and foster sustainability across their value chains. The researchers cover definitions of logistics performance and CSR, discuss the integration of logistics performance and CSR, and provide prior decision tools for evaluating CSR and logistics performance.
Conceptual Framework & Methodology
The Conceptual Framework integrates crucial indicators from both logistics performance and CSR domains, enabling a comprehensive evaluation of supply chain operations. It balances logistics efficiency with sustainability practices, facilitating decision-making that addresses logistics, economic, social, and environmental objectives.
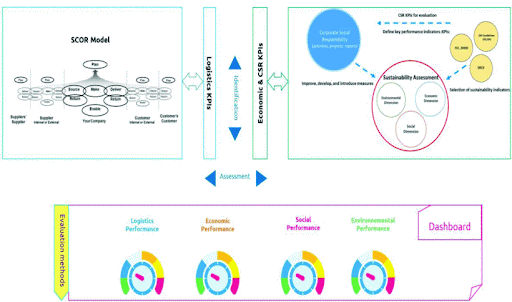
Conceptual framework illustration.
The primary objective is to establish and implement a comprehensive methodological approach for assessing logistics performance and CSR indicators within a responsible supply chain. This approach equips companies with a robust framework to gauge operational performance while ensuring the balanced integration of environmental and social dimensions.
Proposed Decision Tool
According to the researchers, a sustainable manufacturing supply chain was considered for implementing and testing the applicability of the proposed decision support tool. In the use case, a manufacturing company has committed to integrating sustainability principles into its operations, from sourcing raw materials to delivering finished products to customers. Key objectives highlighted in this initiative include reducing carbon emissions, promoting ethical labor practices, and optimizing resource utilization throughout the supply chain.

Example of dashboard featuring Environmental KPIs for the use case.

Example of the Environmental Performance Analysis dashboard with insights and recommendations for the use case.
By applying the decision tool, stakeholders could access multifaceted insights spanning environmental, social, economic, and logistical dimensions. In harnessing data-driven insights, the organization could instill a culture of sustainability across its supply chain, catalyzing positive outcomes in logistics, environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and economic efficiency. This holistic approach could inform strategic decision-making and propel continuous improvement initiatives, potentially fostering sustainable practices throughout the manufacturing supply chain.
Implications and Recommendations
The implications and recommendations from applying the evaluation framework offer valuable insights for organizations aiming to enhance their supply chain performance while advancing corporate social responsibility. As noted by the researchers, the content of such insights include:
Implications:
- Enhanced Operational Visibility
- Alignment with Sustainability Goals
- Stakeholder Engagement and Collaboration
- Continuous Improvement and Innovation
- Resilience and Adaptability
Recommendations:
- Invest in Data Analytics Capabilities
- Foster Cross-Functional Collaboration
- Promote Supply Chain Transparency
- Cultivate a Culture of Sustainability
Conclusion & Perspectives
In this paper, researchers explore the intricate relationship between logistics performance and corporate social responsibility (CSR) within modern supply chain management, addressing the complexities of optimizing operational efficiency while advancing sustainability objectives through a robust evaluation framework.
The findings underscore the need for evolving metrics to encompass broader environmental, social, and ethical considerations, including logistics operations. Moving forward, organizations will need to embark on a journey of continuous improvement and innovation in supply chain sustainability. Fostering a transparency, accountability, and ethical leadership culture is crucial to driving positive change in an increasingly interconnected world. The decision tool presented provides a centralized, automated, and accurate approach to collecting, analyzing, and presenting the data required to make informed decisions.
The researchers also emphasize the need for collective action to shape a more equitable, resilient, and sustainable future facing global challenges. They highlight the strategic and moral imperatives of integrating logistics performance and CSR, stressing that developing calculation methodologies and aggregating logistics are critical for making informed decisions that align business objectives with sustainability practices.
Interested in learning more about the Logistics? IEEE offers continuing education with the IEEE eLearning Libary to smartly implement digital tools into your organization.
Interested in acquiring full-text access to this collection for your entire organization? Request a free demo and trial subscription for your organization.




