5G is transforming telecommunication networks and stimulating innovation across different sectors. 5G wireless networks can provide very high data rates and excellent coverage with increased capacity, better quality, and low latency. This 5G ecosystem offers many opportunities for the economic system. However, it brings new security issues to the mobile ecosystem with broader attack surfaces, more devices, and increased traffic loads.
At the 2023 IEEE 21st World Symposium on Applied Machine Intelligence and Informatics (SAMI), researchers presented a paper on the potential of 5G networks and their issues. The paper focused on providing cybersecurity assurance at all levels of the product lifecycle and building trust throughout the ecosystem. Additionally, the researchers shed light on how implementing 5G networks should ensure security across policy, technology, and standards.
The 5G Ecosystem
The paper begins by explaining how telecommunication ecosystems are becoming significantly more complex, and there is no comprehensive way to describe their value chain. The 5G ecosystem offers many opportunities but also provides risks. In addition to public policy and regulatory agencies, according to the authors, there are five main stakeholders in the 5G ecosystem: providers of civil infrastructure, connectivity providers, service enablers, service creators/application providers, and technology providers.
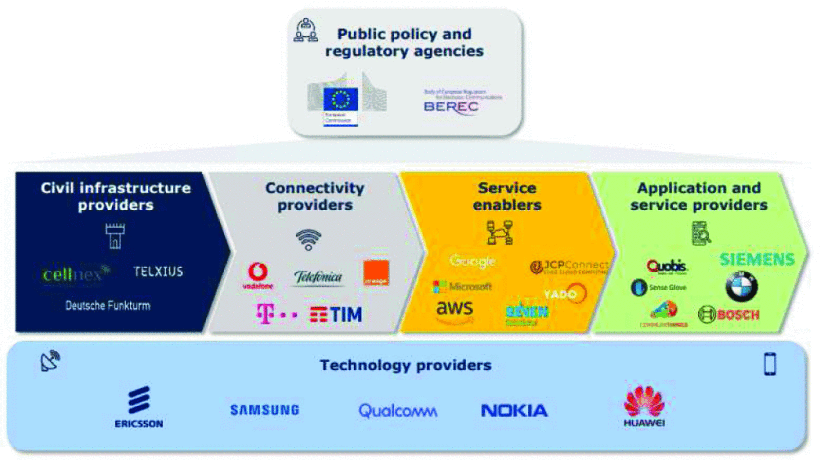
Main stakeholders involved in providing 5G services
As noted by the authors, in the new 5G ecosystem, the value structure changes according to each vendor's perspective, and vendors can function in more than one space:
- Providers of civil infrastructure
Providers can take an evolutionary approach to infrastructure investment by upgrading the capacity of their existing 4G deployment. The additional revenue upside of 5G remains ambiguous, but the actual deployment levels will be driven by improvements to the access network densification and fiber transmission network.
- Connectivity providers
5G is expected to provide progress across the Internet of Things (IoT) and Machine-to-Machine (M2M) applications, influencing new players that can offer new applications for 5G connectivity. Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) should change their networks to fulfill the potential offered by the 5G transition.
- Service enablers
The service enablers part of the ecosystem often changes because of high offers, new services, and evolution. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) have opportunities to offer niche services, such as network slicing and optimization, security, and data analytics.
- Service creators/application providers
In the future 5G network, service creators and application providers must collaborate with an immense suppliers' ecosystem to deliver new services to satisfy IoT solutions.
- Technology providers
Technology providers will have to deal with increased software solutions to networks and applications, data storage, and compute cycles conversation that takes advantage of cloud computing (cloudification).
The Need for Cybersecurity Assurance
The authors note that up to 48% of 5G operators admit their most critical challenge is not having enough or proper knowledge or tools to manage security vulnerabilities. Due to the emergence of cloud, data, and IoT threats, there are new actual and potential security risks associated with 5G. Key topics concerning cybersecurity assurance include security by design and security in the process, standardization, and measures/mitigating plans.
The researchers cite the existing European Union (EU) toolbox for risk-mitigating 5G networks as an excellent start to combat security risks. The measures shed light on security stakeholders and mitigating measures to be taken in the 5G ecosystem. According to the authors, measures should be in place to provide cybersecurity assurance at all levels of the product lifecycle.
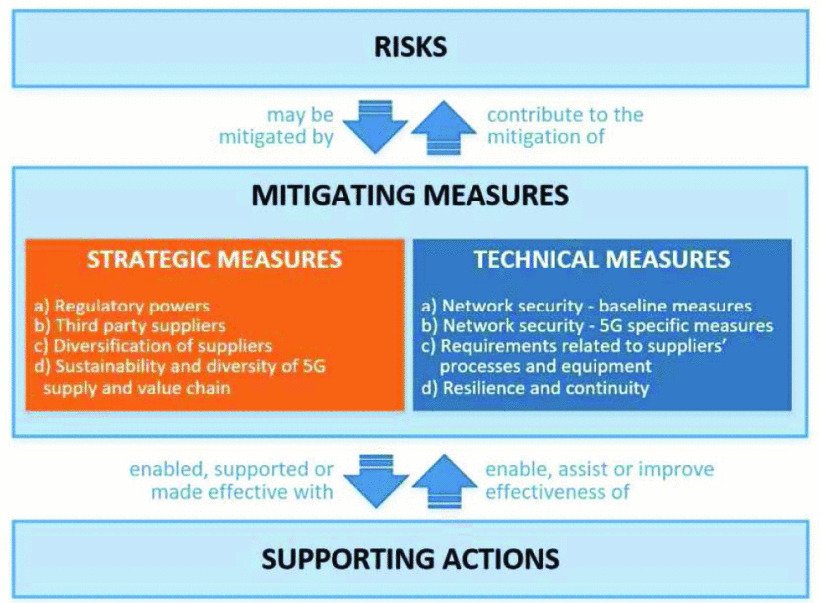
EU toolbox measures and supporting actions
Vendors should be positioned to address and lead critical priorities relevant to the 5G ecosystem. Regulatory actions can offer more reliable types of equipment and applications in terms of cost, infrastructure, connectivity, and security. Also noted is the need for standard vendor development processes and network functions.
As stated early and often in the paper, the 5G ecosystem offers many opportunities for the economic system. 5G technology will offer transformative innovations, enhance productivity, and improve everyday life. The researchers suggest that organizations embrace security by design and security in process mindset to build trust throughout the ecosystem.
Interested in acquiring full-text access for your entire organization? Full articles available with purchase or subscription. Contact us to see if your organization qualifies for a free trial.
Interested in expanding your knowledge on Wireless Communications? IEEE offers continuing education with the Intensive Wireless Communications Course Series.





