First named in 1999 by computer scientist Kevin Ashton, the Internet of Things (IoT) connects thousands of devices, such as thermostats, voice-activated speakers, and medical devices, to a wide range of data. Now, the IoT is set to transform the Metaverse as it seamlessly connects the 3D world to real-life devices. Research suggests the IoT will enable us to overcome one of the greatest challenges we face in the Metaverse—how to map data from real life, in real time, into a digital reality. IoT’s primary role will be to bring the outside world into the digital realm.
In recent years, the Internet of Things (IoT) has been studied in the context of the Metaverse to provide users with immersive cyber-virtual experiences in mixed-reality environments. Two popular applications, augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), are developed to bring immersive digital experiences and social connections to the Metaverse’s users.
In an IEEE Internet of Things Journal, researchers present a survey introducing six IoT applications in the Metaverse. The article also outlines four pillar technologies that enable augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) to work for the Metaverse.
IoT Applications in Metaverse
To support wireless and seamlessly connected immersive digital experiences, the IoT can be leveraged in the Metaverse. The IoT can supplement the experiential interface of the users into the virtual world created by AR/VR. According to the researchers, the Metaverse can be applied to several transaction scenarios in the digital economy: collaborative healthcare, education, smart city, entertainment, real estate, and socialization.
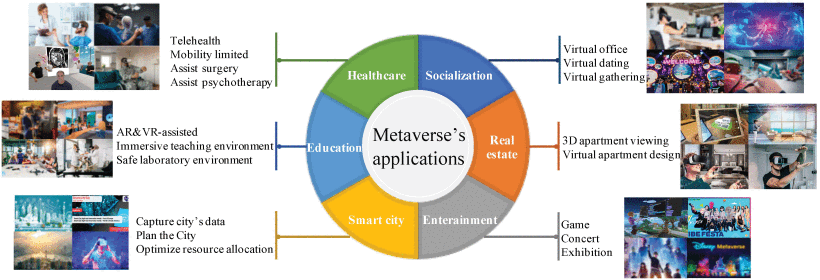
Six typical applications of the Metaverse include healthcare, education, smart city, entertainment, real estate, and socialization.
The article starts by providing discussions of each projected application:
- Healthcare: The World Economic Forum has predicted that digital services will be one of the most critical factors in transforming healthcare over the next decade. Before the COVID-19 pandemic, 43% of healthcare facilities could provide telehealth, which rose to 95% in 2020. The Metaverse promises to facilitate the development of telehealth with benefits for patients, doctors, healthcare staff, and medical students.
- Education: Metaverse technologies in the education sector have gained significant momentum. AR/VR which emphasizes visualization-based learning concepts will be widely used to transform traditional teaching approaches, creating engaging and immersive learning environments for students.
- Smart City: As a supporting technology in the Metaverse, IoT-empowered digital twins can utilize the IoT data to digitize the objects in the physical world, such as roads and streets, houses, vehicles, and city infrastructures, and create virtual cities. Essentially, the Metaverse is used in the smart city to optimize the allocation of facilities and resources.
- Entertainment: The development of Metaverse-related technologies has dramatically improved the immersion of games, which can effectively enhance user experience, playability, and fun. AR/VR technology can provide an immersive environment for large events, such as exhibitions, concerts, and book signings.
- Real Estate: As one of the key technologies driving the Metaverse, AR/VR provides customers with a realistic and immersive experience allowing real estate agents to give the buyers a virtual tour of a property. The Metaverse can also be used to conduct inspections and in interior design and architectural fields.
- Socialization: The Metaverse breaks the boundaries of time and space, which can provide various forms of social interaction, bringing people closer to each other. People can pursue remote social platforms to create a more authentic social environment.
Four Pillar Technologies of Metaverse
To achieve a convergence of physical and cyber worlds, the IoT-inspired Metaverse must meet four basic requirements: trust and usability, low-latency data transmission, imperceptible response times for the data, and combining digital replicas with physical products and services. According to the authors, four pillar technologies are essential cornerstones for supporting the mainstream services and applications in the IoT-inspired Metaverse: Responsible AI, High-speed data communications, Cost-effective MEC, and IoT-based digital twins. These technologies can be leveraged to bridge IoT applications with the Metaverse.
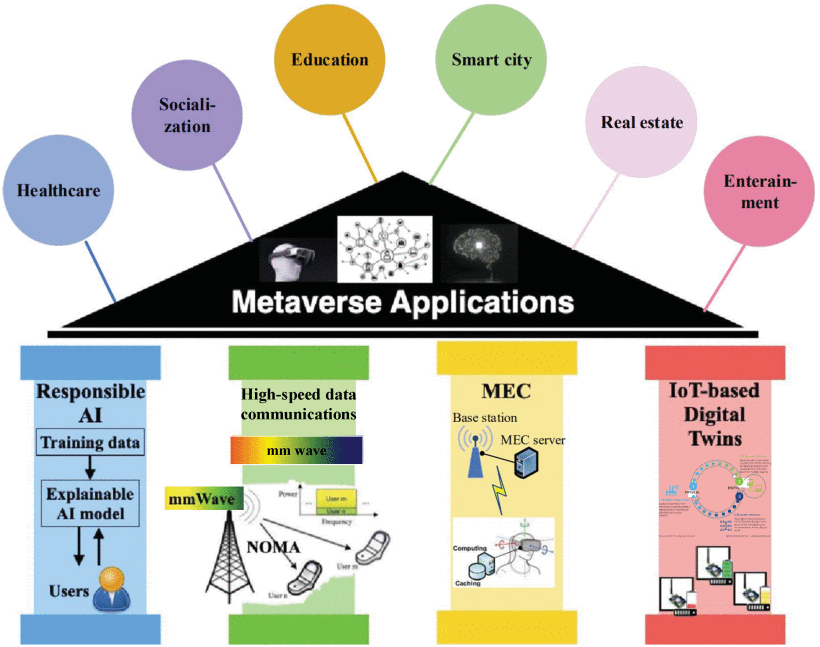
Four pillar technologies that support the IoT applications in the Metaverse.
Responsible AI helps engineers and data scientists explain what is happening inside the AI algorithm, while high-speed data communication empowers real-time connections. MEC provides the Metaverse with massive server resources to power the virtual 3-D realm and delivers ultralow latency communications for imperceptible response times. Finally, digital twins can create virtual replicas of physical objects or services. The authors outline the motivation, significance, key technologies, and typical applications for each pillar technology.
The Future of the IoT-Empowered Metaverse
This article presents the IoT-inspired applications that can provide users with immersive cyber-virtual experiences while outlining key technologies that the IoT-Empowered Metaverse will rely on. The authors also suggest critical open issues that any further development and implementation of the IoT-empowered Metaverse need to address. These issues include Data Processing, Security and Privacy, Real-Time 3-D Modeling, Scalable Cyber Worlds, Connected Mobile Users’ Experience, Interoperability and Uniformity of Virtual Platforms, and Barriers to the Physical World.
Interested in acquiring full-text access for your entire organization? Full articles available with purchase or subscription. Contact us to see if your organization qualifies for a free trial.





