With the development of both present and future technologies, the Internet of Things (IoT) based solutions offer many potential benefits to today’s world, especially in healthcare. Currently, there is a high demand for low-cost solutions in connected healthcare and real-time wireless patient monitoring remotely. Intelligent wireless body monitoring leads to better healthcare, as insights into the body mean that devices can serve as preventive health tools.
Radiofrequency identification (RFID) is a rapidly emerging wireless technique utilized in different applications such as healthcare, automated identification, object tracking, security and authentication, food packaging, and automobile tracking. While the projected cost of conventional RFID technology hinders it from being widely used, RFID sensors can meet the growing demand requirements when paired with the Internet of Things (IoT) technology. In an article published in IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, researchers have provided a comprehensive review of the chipless RFID sensors playing a vital role in cost-effective healthcare applications.
The Need for Personalized and Connected Healthcare
Today, there are countless, albeit expensive, sensors for measuring physical parameters and biological parameters such as blood pressure (BP), heart rate, glucose level, pH of body fluids (blood, gastric juice, saliva, and urine), and body temperature. Readings of these physical parameters can dictate a whole slew of medical diagnoses and treatments. The authors posit that although the demand for less expensive sensing systems is prevalent—the price of those systems, and the ability to be part of the IoT for collecting information with cloud computing, remain roadblocks in the developing sensor domain.
The traditional methods used in healthcare for sensing vital signs can be invasive and tedious, especially for senior citizens. Newer RFID-based methods, according to the article, excel more than the traditional approaches because they are non-invasive, convenient, capable of multiple tag reading, and operable across a relatively large range. The chipless RFID sensors are typically less expensive and provide a long lifespan due to the absence of application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) chips. Taking advantage of the IoT and chipless RFID sensors offers numerous opportunities for automatic identification, remote sensing, networking, and processing.
With the advent of wearable technologies, real-time monitoring and tracking of patient health conditions are manageable. The chronically ill senior citizens find it difficult to have regular dates with the doctor in hospitals. The number of hospital visits can be significantly reduced when the patients can be monitored remotely using innovative technologies. Moreover, the health Internet of Things (H-IoT) is particularly favorable for senior citizens as they can care for their health at home rather than staying a long time in hospitals. People can grant access to their health data using various mobile applications to trusted medical practitioners through the advancement of connected health for the early detection of diseases.
Wireless Communication & Wearable Technologies
The advancement of the IoT and innovative technologies in wireless communication has recently transformed the healthcare sector. The IoT promotes the interaction of several smart sensors, such as chipless RFID sensors, eliminating the requirement of manual intervention, and enabling the exchange of sensing information with trusted healthcare users. According to the authors, a basic IoT-based system can be grouped into four subgroups (things, gateways, communication networks, and cloud/data analytics platforms).
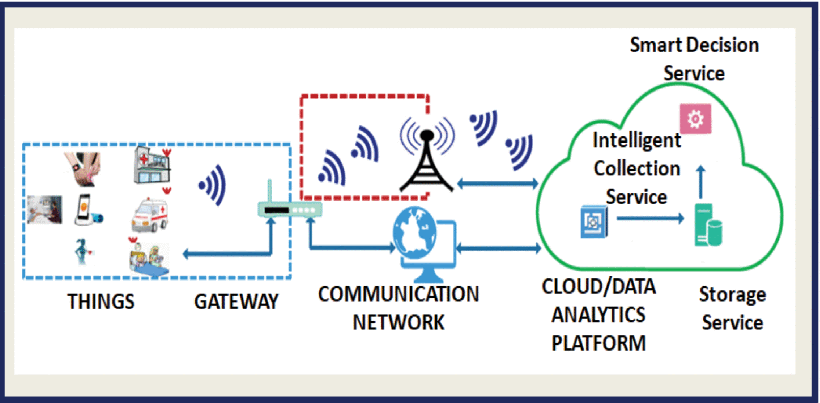
Outline of IoT-based healthcare system
The introduction of compact chipless sensors and the ability to link to the Internet of Things has increased the possibilities of intelligent healthcare. The wearable devices, such as real-time patient monitoring systems and miniaturized gadgets that continuously track a patient's health, give a new face to healthcare applications. According to the authors, wearable systems in the healthcare sector include heart and respiratory rate monitoring systems, stroke rehabilitation systems, electrocardiography (ECG), electromyography (EMG), and electroencephalography (EEG) signals for monitoring the health condition of the heart, muscle, and brain, respectively.
Various biological parameters also can be measured by sensing systems; with the patients using more than one wearable system—their health data will be tracked, recorded, and examined by the doctors in real time. In an emergency, patients can automatically get help from medical practitioners. Chipless RFID sensor tags are desirable in these scenarios because they consume less energy and have longer battery life.
IoT-Based Smart Healthcare System
The IoT and low-cost chipless RFID sensors can improve the healthcare sector by implementing several connected personal smart health systems. Chipless RFID sensors can be easily integrated into clothes or personal things (smart watches or jewelry) so that monitoring continuous health status becomes possible. The chipless sensors are more durable and flexible than traditional chip sensors, requiring less power.
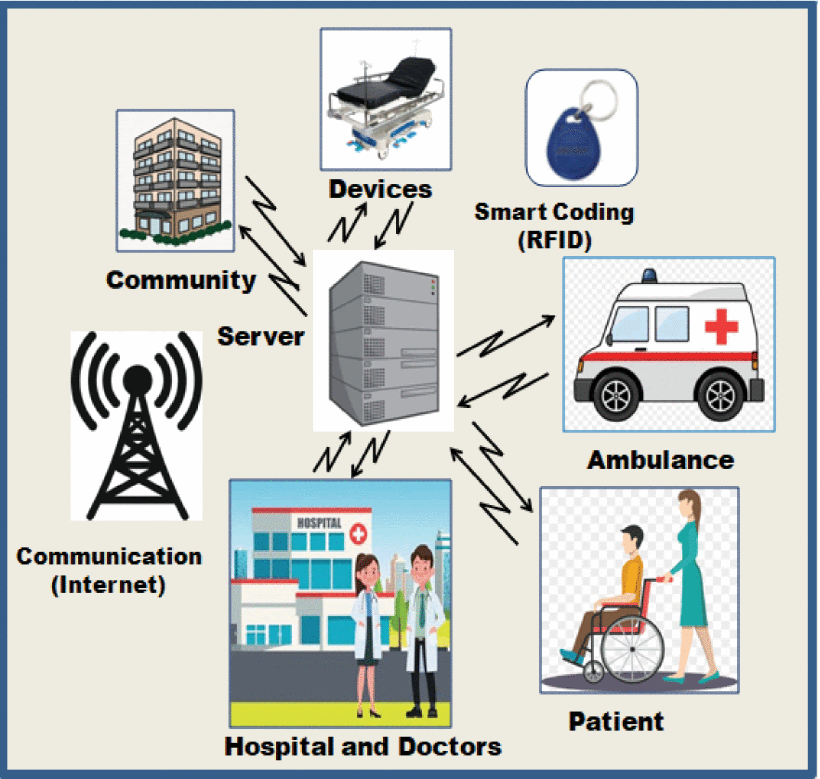
Prototype of IoT-based smart rehabilitation system
In the article, the authors propose a smart system that consists of medical assets, such as hospitals, rehabilitation hubs, medical practitioners, emergency transportation services, therapeutic instruments, patients, and a server. RFID tags are used for the remote monitoring of patients, and GPS is used for tracking the location of medical utilities or patients. This interconnecting of technology helps the integration of healthcare using existing treatment methods.
Future Directions & Challenges
The progress of IoT has paved the way for numerous accomplishments in chipless RFID sensors for healthcare. In addition to highlighting possible use cases, the authors discuss the geometry, design, system architecture, and sample results for future directions, such as:
- IoT-Based Smart Skin Sensors
- Wearable Chipless Tag for IoT Applications
- Biological Sensing System Based on IoT
- RFID Tags for Sitting Posture Recognition
- Chipless Tags for Surgical Tracking
- RFID Tags for Sleeping Posture Recognition
Demand for radio frequency identification (RFID) sensors in the healthcare sector is expected to expand, with a growing focus on patient tracking. The authors note that additional IoT-based systems research opportunities exist, including security features, confidentiality, real-time analysis, required training time, and wearability. Likewise, opportunities exist for more chipless sensor research focused on simultaneous data capture of multiple tags, fabrication, reproducibility, feature extraction, and tracking distance.
View the full-text article on IEEE Xplore. Full article available with purchase or subscription. Contact us to see if your organization qualifies for a free trial.





